STP (Spanning Tree Protocol)
STP (Spanning Tree Protocol) is used to prevent any network for looping of frames by keeping some ports or interfaces of device in forward state and some ports or interfaces in blocked mode.
When two or more than two switches are connected with each other to create redundant links then it may cause loop occurrence. STP is layer 2 protocol and it enabled on switches by default. STP is used to stop loop occurrence.
- STP - IEEE 802.1D (Open Standard)
- RSTP - IEEE 802.1W
- MST (Multiple Spanning Tree) - IEEE 802.1S
- PVST (Per VLAN Spanning Tree) - CISCO Proprietary
- PVST+ - CISCO Proprietary
- RPVST - CISCO Proprietary
- CST (Common Spanning Tree) - All VLANs will participate in single number of instance
- IST (Inter Spanning Tree) - Different - Different VLANs Different - Different number of instance
Problems which occur if STP is not used
- Storm of Broadcast
- High Process Utilization
- Instability of MAC Table
- Transmission of Multiple Frames
Tasks performed by STP
- Root Bridge Elect
- Designated Port Elect
- Root Port Elect
Root Bridge Elect
A switch having lowest best bridge ID which is the combination of switch priority and MAC addresses. This ID is consist of 8 bytes. 2 bytes for priority and 6 bytes for MAC address.
By default priority of switches is 32768.
Priority can be changed and set between 0 - 65535.
Designated Port Elect
Ports which advertise BPDUs having lowest cost are know as designated ports. BPDUs are sent by designated ports towards Non Root Bridge.
Root Port Elect
Port that receives the BPDUs of lowest cost is know as root port. It is the shortest path to the root bridge.
COST - Cost is an integer value which is used to perform Designated Port (DP) and Root Port (RP) elections.
| Ethernet Standards | Cost |
| 10 Mbps | 100 |
| 100 Mbps | 19 |
| 1 Gbps | 4 |
| 10 Gbps | 2 |
BPDU (Bridge Protocol Data Unit)
Each switch send hello packet to other switch in every 2 sec and that hello packet is known as hello BPDU.
There are two types of BPDU
- Configuration BPDU - Sent from Root to Non-Root
- TCN (Topology Change Notification) BPDU - Sent from Non-Root to Root
Contents of Configuration BPDU
- Protocol ID is always 0
- Version is always 0
- Type of Message
- Flag
- ID of Root Bridge
- Cost of Root
- ID of Sender Bridge
- Priority of Sender Port
- Maximum Age
- Age of Message
- Hello
- Forward Delay
Content of TCN BPDU
- ID of Protocol
- Version
- Type of Message
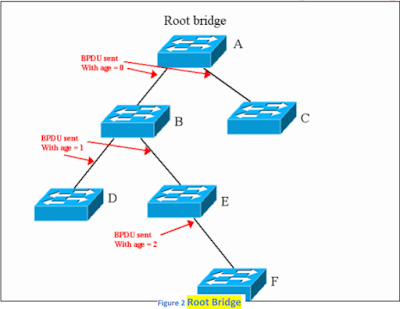
- Root Bridge sends configuration BPDU after every 2 seconds.
- Cost of BPDU send by root bridge is always 0.
Root Bridge Requirements
- Low Bridge Priority
- Low MAC Address
(NOTE: COST OF BPDU GENERATED BY ROOT BRIDGE IS ALWAYS 0)
DP and RP Requirements
- Lower Bridge ID which is only for DP and between Root and Non Root
- Low Cost for DP and RP
- Lower Sender ID between Root to Non Root
- Lower Sender Port Priority between Non Root to Non Root
- Lower Sender Port ID
Configurations of STP
As we have learnt above that STP is enabled by default on all the switches, so here we will see that how the cost and priority of any interface can be changed or how to make any switch as root bridge.
If we want to make switch as root bridge for one vlan
Switch(config)# spanning-tree vlan 1 priority 0
If we want to make switch as root bridge for all vlans
Switch(config)# spanning-tree vlan 1 - 4094 priority 0
To remove switch from root bridge
Switch(config)# no spanning -tree vlan 1 - 4094 priority 0
If one switch goes down then other switch becomes root bridge
Switch(config)# spanning-tree vlan 1 - 5 root primary
Switch(config)# spanning-tree vlan 6 - 10 root secondary
On other switch issue the reverse commands
Switch(config)# spanning-tree vlan 1 - 5 root secondary
Switch(config)# spanning-tree vlan 6 - 10 root primary
To change the cost of any interface
Switch(config)# interface fa 0/1
Switch(config-if)# spanning-tree vlan 1 cost 20
Switch(config-if)# exit
To change the priority of any port
Switch(config)# interface fa 0/1
Switch(config-if)# spanning-tree vlan 1 port priority 100
Switch(config-if)# exit
To configure port fast
Switch(config)# interface fa 0/1
Switch(config-if)# spanning-tree portfast
We can also configure range to configure port fast
Switch(config)# interface range fa 0/1 - 24
Switch(config-if-range)# spanning-tree portfast
Switch(config-if-range)# exit
To stop or disable spanning tree protocol
Switch(config)# no spanning-tree vlan 1
Set timer for Hello Packet
Switch(config)# spanning-tree vlan 1 hello time <select form 1 to 10 sec>
Change Maximum age
Switch(config)# spanning-tree vlan 1 max-age <select from 6 to 40 sec>
Change forward delay time
Switch(config)# spanning-tree vlan 1 forward-time <select form 4 to 30 sec>

No comments:
Post a Comment